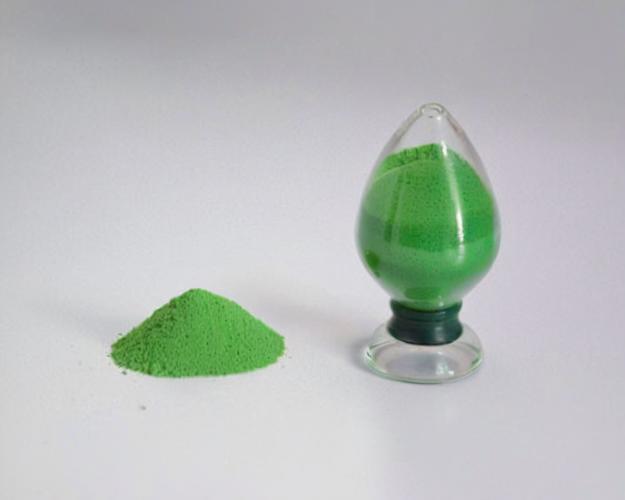
Nickel chloride, also known as nickel(II) chloride, is a chemical compound that occurs in various forms, including anhydrous and hydrated forms. The anhydrous form is a yellow crystalline solid, while the hexahydrate form is a green crystalline solid. It is highly soluble in water and forms a brownish-yellow aqueous solution.
In the electroplating industry, nickel chloride is a key component in the process of applying a layer of nickel onto the surface of objects, such as metal components and automotive parts. Electroplated nickel provides corrosion resistance, durability, and an appealing finish. It is also utilized in the production of nickel-cadmium (NiCd) and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries, which are commonly found in portable electronic devices, cordless power tools, and other applications.
In chemical reactions, especially in the synthesis of organic compounds, nickel chloride is employed as a catalyst. It helps facilitate and accelerate various chemical transformations. Additionally, it serves as a precursor for other nickel compounds used in the chemical industry, such as nickel carbonate and nickel oxide.
Regarding safety, exposure to nickel and its compounds should be managed with care due to potential toxicity and the risk of allergic reactions in certain individuals. Proper safety measures and precautions are essential when handling nickel chloride to ensure the safety of workers and the environment. For storage, it should be kept in a cool, dry place to prevent degradation and should be stored away from moisture and in a well-sealed container to maintain its quality and effectiveness for various applications.