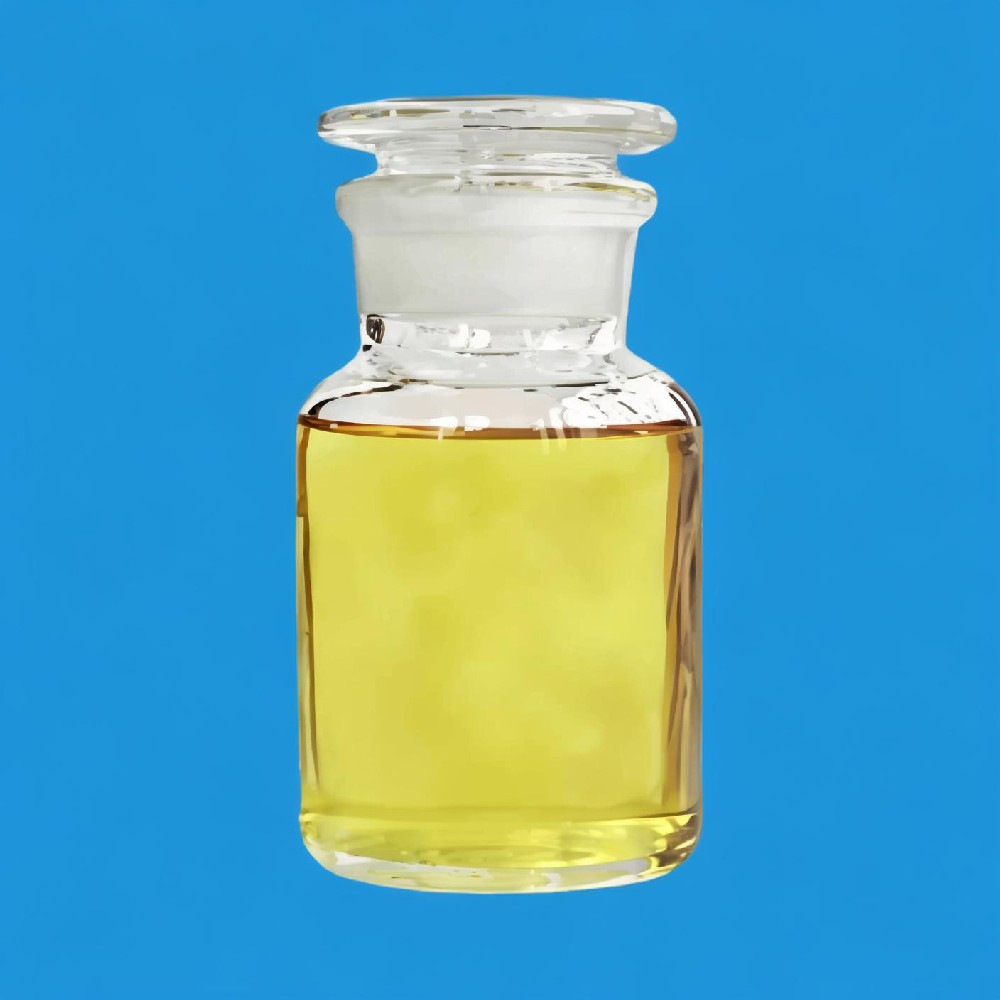
Monomer Acid refers to a class of organic compounds that can react with other molecules to form very large molecules, or polymers. These compounds are characterized by their polyfunctionality, the ability to form chemical bonds with at least two other monomer molecules. They are the building blocks for polymers, which are created through addition or condensation reactions.
Monomer Acids are typically derived from natural sources or synthesized chemically. They are used in a wide range of applications, including the production of paints, inks, adhesives, coatings, and various types of plastics. They are also used in the manufacturing of alkyd resins, synthetic fibers, and elastomers.
In terms of physical properties, monomer acids can exist as liquids or solids at room temperature and are generally soluble in organic solvents but not in water. They have a melting point and boiling point, with specific values depending on the specific monomer acid. For instance, methyl acrylate, a type of monomer acid, has a melting point of 12-16 °C and a boiling point of 163 °C.
Monomer acids are also important in the biomedical field. They can be used to synthesize bio-based polymers for applications in drug delivery, tissue engineering, and other medical devices. Their biocompatibility and biodegradability make them suitable for use in products that interact with living organisms.
In summary, Monomer Acids are fundamental organic compounds used in the synthesis of polymers and have a broad spectrum of applications in various industries, from coatings and plastics to biomedical applications.