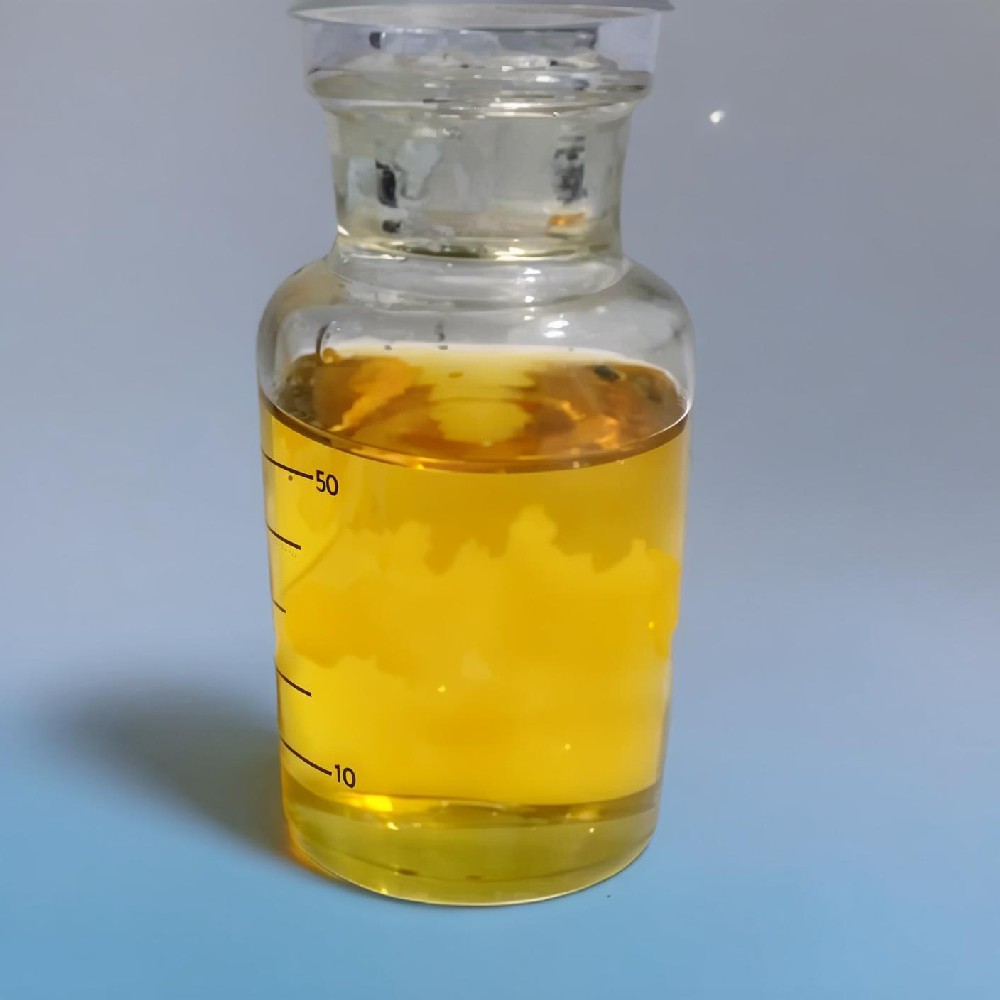
Dimer Acid, also known as dimer fatty acid, is a complex mixture derived from the dimerization of unsaturated fatty acids, such as oleic and linoleic acids. It is an important oleochemical used in various industries due to its unique properties and applications.
Dimer Acid is characterized as a colorless, transparent liquid with a relative density of 0.95 and a flash point ranging from 280-350°C. It is soluble in a wide range of solvents, including acetone, ethanol, ether, and hydrocarbons like kerosene and petroleum.The molecular formula of dimer acid is C36H64O4, with a molecular weight of 560.91.
This dimeric acid exhibits excellent thermal stability, remaining fluid at temperatures as low as -20°C and not evaporating or gelling up to 250°C. It is also known for its low vapor pressure and good lubricating properties.Dimer Acid does not dissolve in water but is compatible with a variety of organic solvents, making it versatile for use in different formulations.
Industrially, Dimer Acid is primarily used in the synthesis of polyamide resins, which account for 80-90% of its total consumption. It is also used as an additive in fuel oils, lubricants, and cutting oils, as well as in the production of surface active agents, synthetic paints, inks, adhesives, and curing agents.The ester forms of dimer acid serve as viscosity stabilizers over a broad temperature range, and its metal salts are widely used as thickeners in lubricating greases.
In summary, Dimer Acid is a versatile, thermally stable, and chemically reactive compound with a wide range of industrial applications, particularly in the production of polyamide resins and as an additive in various oil-based products.